Found a job that seems too good to be true? Sad to say, it probably is.
With most job searches going online, job scams are on the rise — and as our digital literacy improves, so does the sophistication of these scams.
In 2021 alone, the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) received 2.8 million reports of fraud, including job scams. Amidst all that, how can you protect yourself from scammers and ensure that job postings are legit? Keep scrolling to learn:
- The most common types of job scams (with examples of what to look out for)
- How to identify a job scam
- Steps to keep your private information safe
- Where to find legitimate jobs
- What to do if you think you’ve been scammed
Well start by taking a look at some of the most common job scams — and the biggest red flags to avoid.
Look out for these red flags — they're usually scams
The biggest red flags when looking for jobs are:
- The company demands any kind of payment upfront
- The recruiter asks for personal information
- The website or email address doesn't look real
- The email or job posting has a lot of spelling, grammar, or syntax errors
- The job description is overly vague
- The company is too eager to hire or the job otherwise seems too good to be true
If you spot any of those — or if anything feels a little bit off — stop immediately and take a critical look at the job.
We'll discuss each of these warning signs in more detail later, but first, let's see what some common job scams look like in action.
10 most common job scams (and how to avoid them)
Money transfer scam
There are a lot of cash handling and money transfer schemes around, from the infamous "Nigerian Prince" scams to more legitimate-looking job scams. Here's an example:
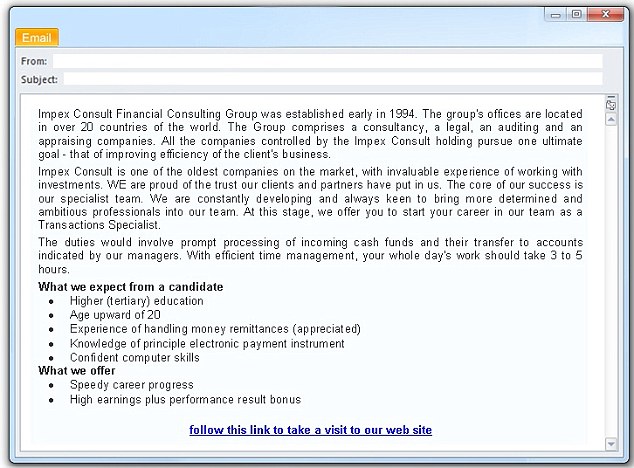
Some jobs do require money handling — but that's not all they involve. A job posting that requires no previous experience and is only seeking someone part-time to move money around on their behalf is definitely a scam.
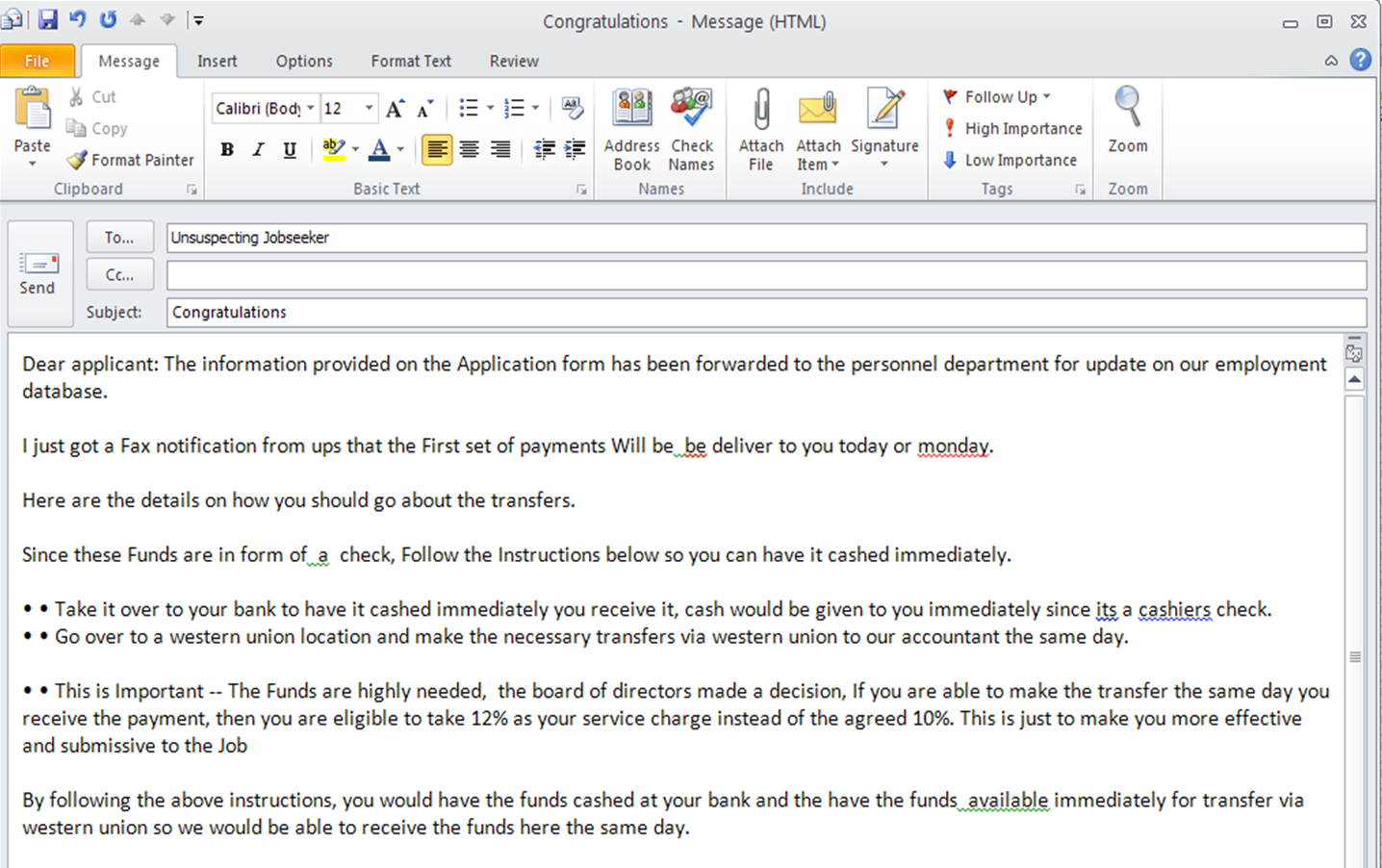
Fake check scam
Some jobs do still pay via check, so that in itself isn't a red flag. What is a red flag is being asked to make a transfer of any kind after cashing the check — inevitably, these checks will fail to clear and you’ll be out for the amount you sent.
Online data entry scam
Avoid any data entry jobs that ask for a training or registration fee — legitimate employers will pay you for training, not the other way around.
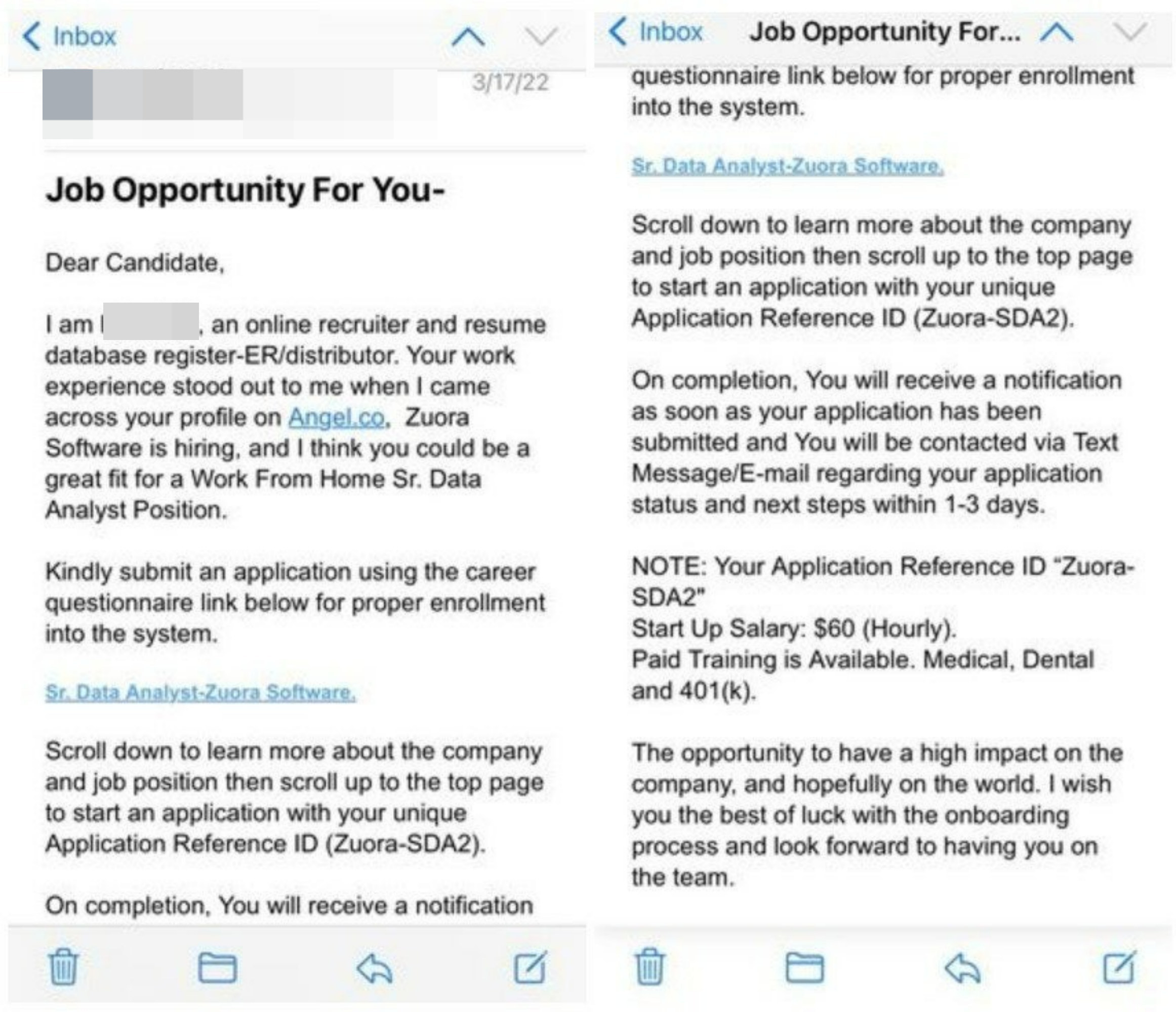
Similarly, any job that seems too good to be true probably is — if you're offered a senior-level job with minimal experience or the hourly salary seems absurdly high, that's a sign you may be looking at a scam.
Shipping scams
These scams ask you to receive packages at home, repackage, and resend them. Not only are these “jobs” inherently sketchy, they often require you to pay the packaging and shipping fees with the promise of reimbursement — which never arrives.
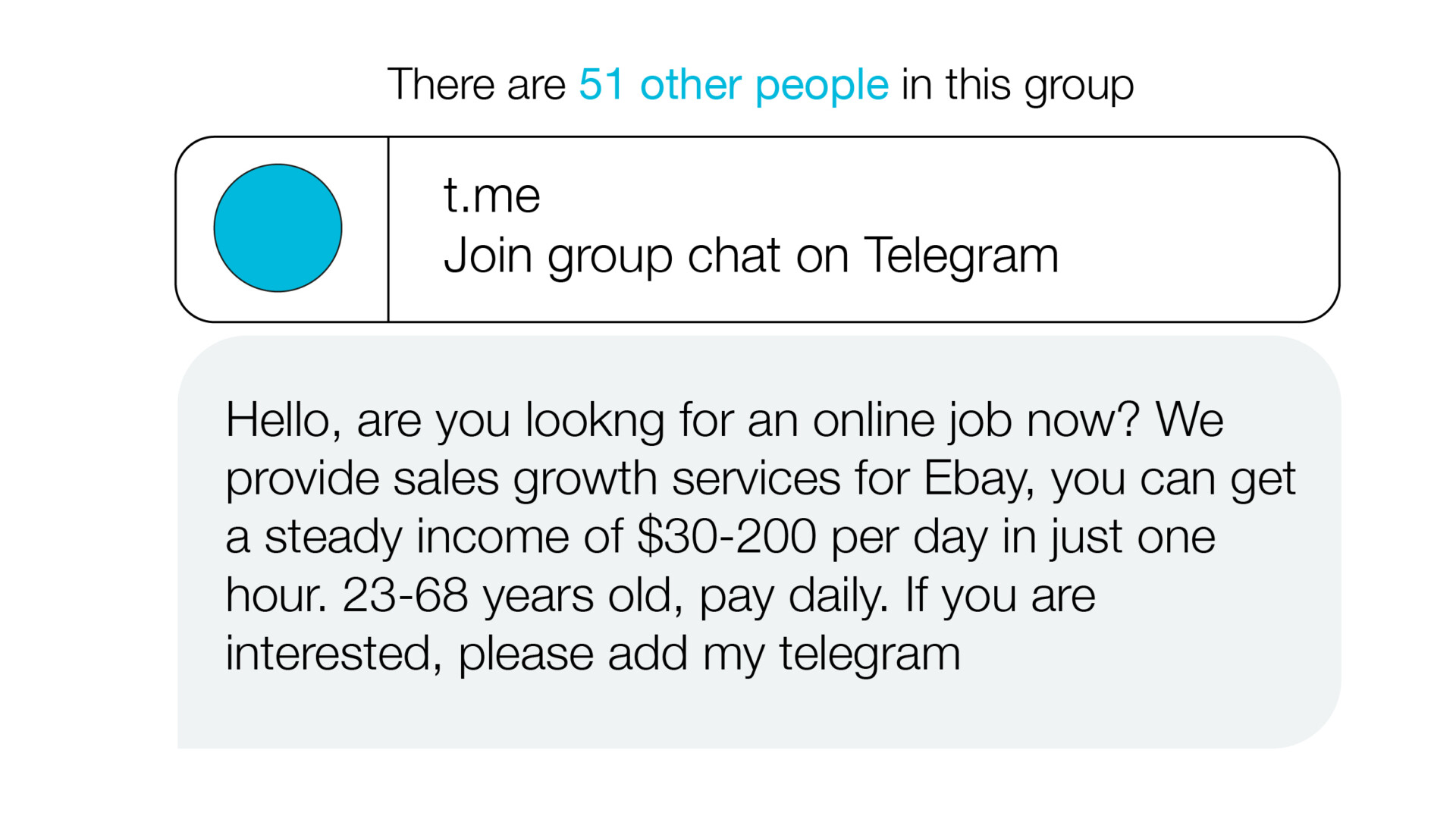
Fake job scams
Never accept any job you haven’t actually applied for. These scammers are usually looking for personal information, like your bank account details, driver’s licence, or Social Security Number.
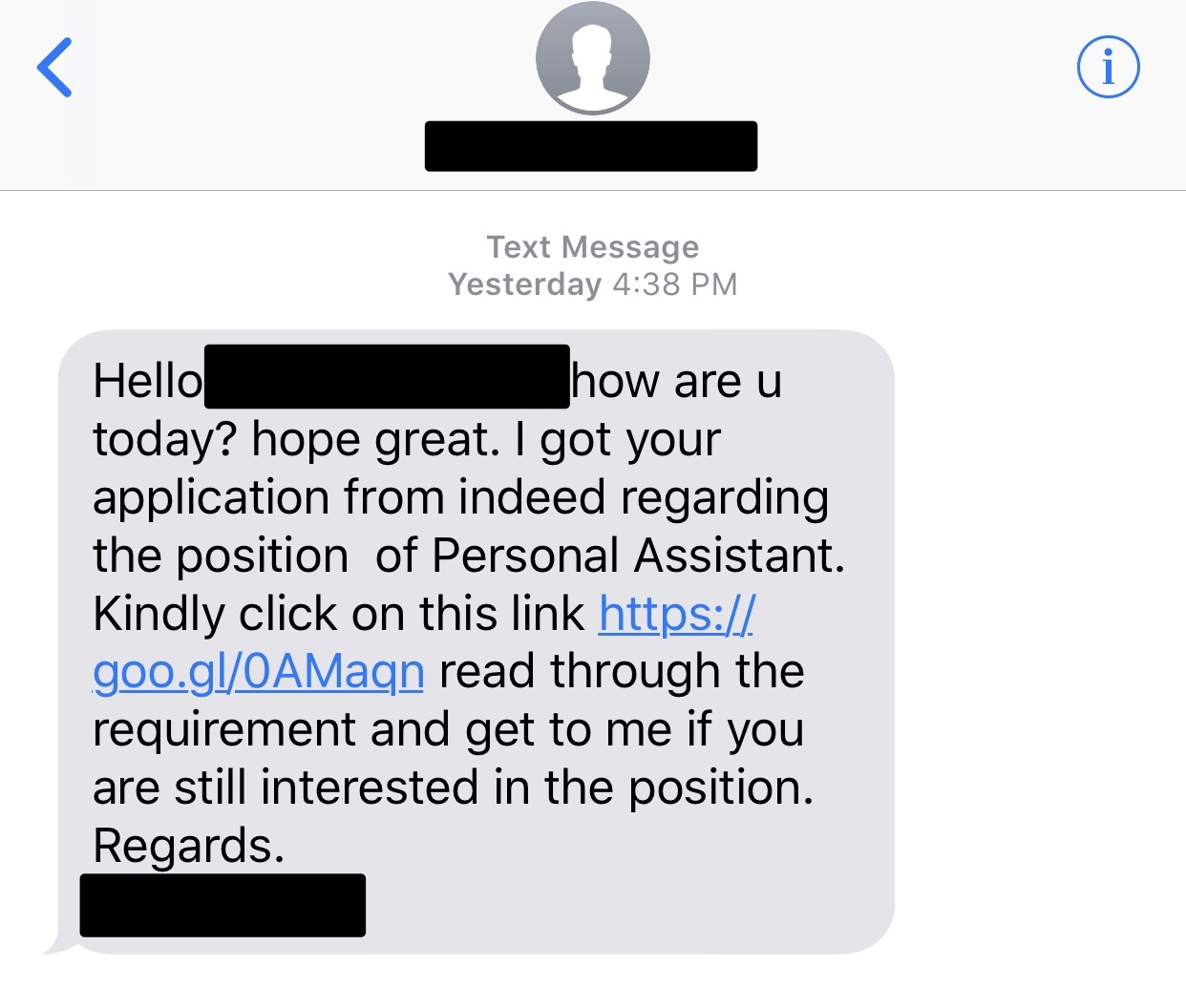
Fake company scams
You may think you're in the clear if you've been contacted by a well-known company, but don't forget to do your due diligence. If you've been contacted out of the blue or are applying via a third party job board or social media website, visit the company's website directly to make sure the job really exists.
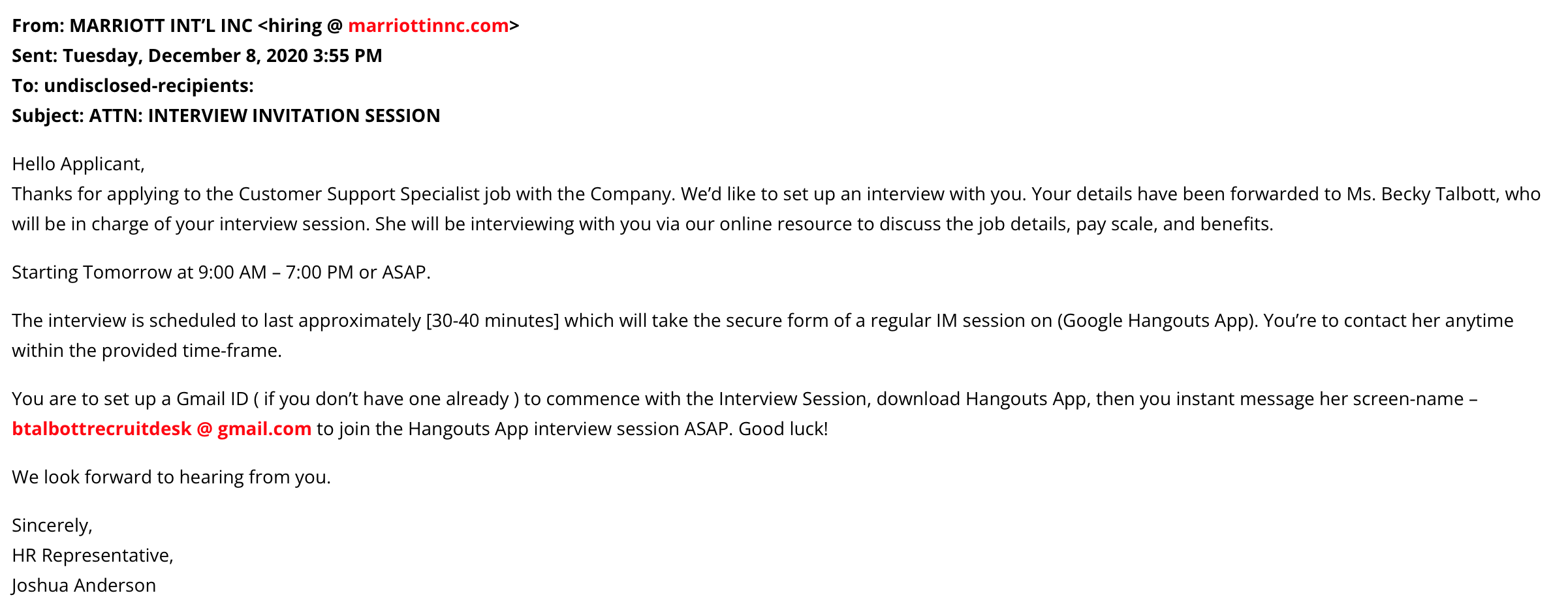
Also keep an eye out for domain names or email addresses that don't look quite right — an internal recruiter will always use an official company email address, not a Gmail or Hotmail address.
Multi-level marketing (MLM) job scams
Commonly known as pyramid schemes, these scams seem like a great way to make a lot of money for very little time and effort — which is a red flag in itself. In reality, they rely on predatory tactics and payment is usually nonexistent.
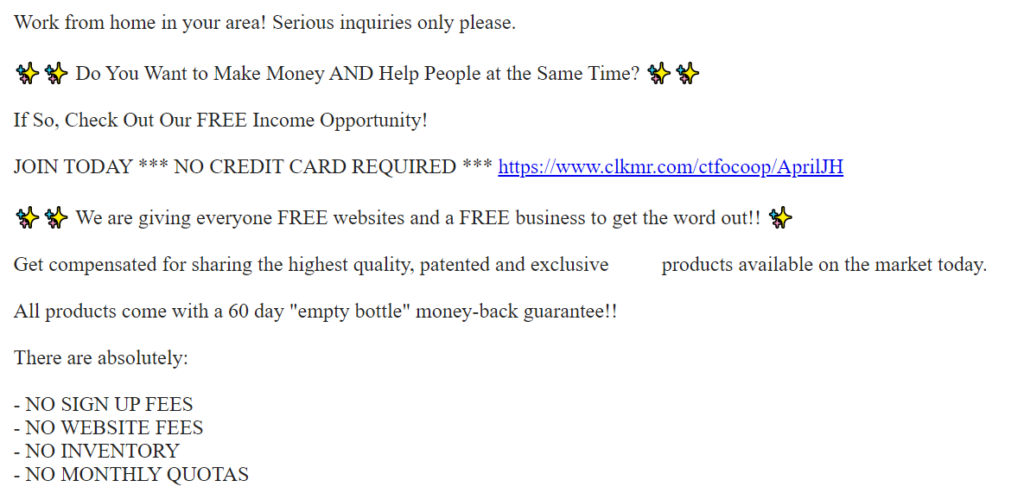
Freelance job scams
Whether you're an experienced freelancer or just starting out, it can be difficult to sort the legitimate clients from the scams. Watch out for overly vague descriptions of the job or company, unusually low (or high) rates, and low ratings or negative feedback.
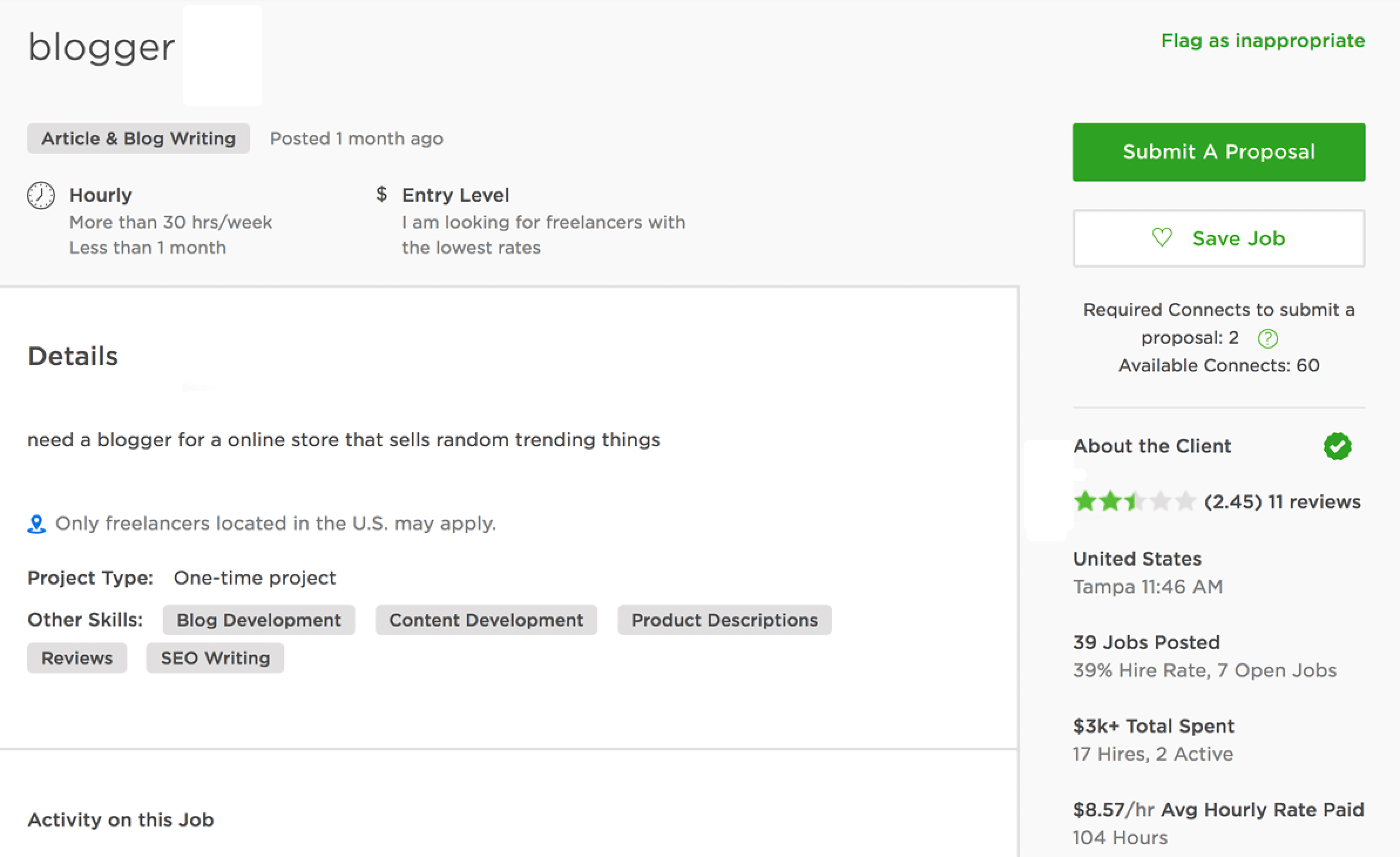
Personal information job scams
Like other phishing scams, these scams rely on people hitting "reply" without really thinking about it. It may seem harmless to reply to a recruiter with your personal email address, phone number, or proof of identity, but often these "jobs" don't exists and are just a front for scammers to gain access to your personal information.
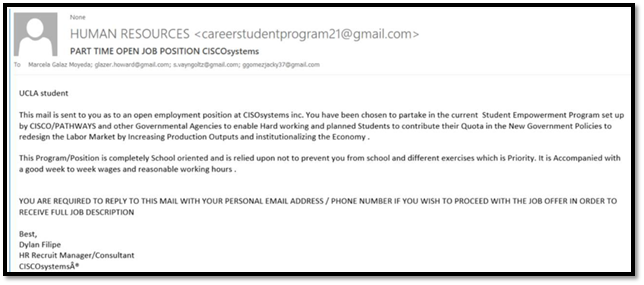
"Too good to be true" job scams
Received a job offer out of the blue for a position you never applied for? Skipped straight to the offer stage without needing to interview? Offered your pick of jobs (that you're underqualified for) from a big name company? Any of these sound like a dream come true for job seekers — which is why they work.
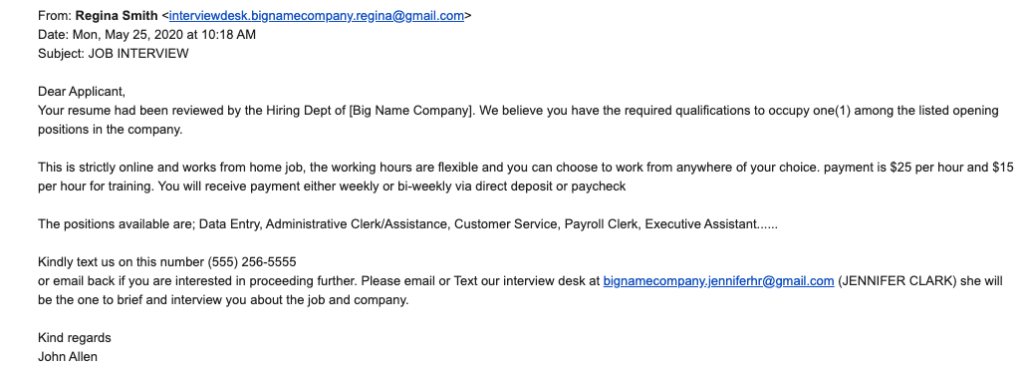
Always be skeptical of something that seems too good to be true. While it could be your big break, it's unfortunately way more likely to be a scam.
Other common job scams
Want to know about more common job scams? Here are some others to look out for.
Work from home job scams
- Reselling scams. These scams offer luxury goods at a discounted price, which you can then resell for a profit.
- Assembly job scams. These jobs seem simple, like assembling products, stuffing envelopes, or making simple crafts, but the employer will often “reject” your finished product — after they’ve received it.
Upfront payment scams
- Registration fee scams. Don’t ever send money upfront for application or registration fees. These fees should be covered by your employer, or at a minimum deducted from your paycheck.
- Equipment scams. The same rule applies to paying for your own equipment. Legitimate employers will pay for any necessary equipment or allow you to use your own, but will never ask for money to cover it.
- Recruitment fee scams. Legitimate headhunters will never ask you to pay them to find you a job.
Fake website job scams
- Job board scams. Sites like Craigslist do feature real jobs, but they also contain scams, so watch out. Even legitimate sites like LinkedIn or Indeed can have fake job postings, so always verify by going to the company website.
- Social media job scams. Be wary of social media accounts with few followers — they’re unlikely to be the real deal. Try Googling the company name to see if multiple accounts show up — some of these are likely to be fake.
- Federal job scams. All federal jobs are free to apply for. To be safe, apply directly for federal jobs on official sites like USAJobs.
Verifying the job posting before applying for jobs through job boards is important. After verifying, upload your resume to the tool below to ensure it is effective and highlights your most relevant accomplishments before sending out your resume.
How to spot a job scam
Not sure how to spot the difference between a job scam and a legitimate posting? Here are some tell-tale signs that you may be looking at a scam:
You’re asked for money upfront
You should never have to pay to land a job — it should be the other way around! This includes:
- Paying a non-refundable registration fee
- Purchasing start-up equipment with the promise that you’ll be reimbursed
- Fake checks — if an “employer” sends you a check and asks you to transfer money somewhere else in return, steer clear!
You’re asked for personal information
The two most common types of scams are financial scams and identity theft. Be wary of providing your:
- Home address
- Bank account information
- Social Security Number
- Passport
- Driver’s licence
- Any other personal identifiable information
As a rule, you shouldn’t need to provide your personal details until you actually start working. If a company asks for this information too early in the process — via email, on an application form, or in an employment contract — you may want to start asking questions of your own.
The website or domain looks wrong
Scammers often use emails or websites that look almost right — but not quite. Look out for:
- Unofficial email addresses. Recruiters will always contact you through their official company email, so you should be looking at an email from [email protected], not [email protected].
- Specifically, any email address ending in @gmail, @yahoo, or @hotmail (unless it’s an external recruiter).
- Errors in the website URL. www[.]microsoft[.]com is legit, but www[.]2micro-soft[.]com isn’t.
- Job postings that don’t appear on the company website. Most companies will list openings on their own websites in addition to external job boards.
- Job postings on unusual websites — for example, an ad to work for Google posted on Craigslist or Gumtree.
Lots of errors
Typos happen, but obvious errors in spelling, grammar, and syntax, or even an overall lack of polish, can all point to a scam. Real job postings tend to be proofread and written by people with good communication skills, so if an ad looks like it was put together hastily or by somebody who obviously doesn’t speak English well, it probably was.
Not enough information
Job postings that are overly vague — about the company, the role, or what they’re looking for — may be lacking details because the job doesn’t actually exist. Try to avoid:
- General ads without a specific job attached. A line like “we have lots of jobs, so send us your resume” may just be fishing for personal information.
- Jobs with overly generic titles, like “Analyst.”
- Ads that lack a job description or where the “minimum requirements” don’t list essential skills.
They seem too eager to hire
We’re not talking about companies that are understaffed or experiencing high turnover — although those can be red flags in their own right. Be wary if:
- A potential employer pushes for things to move too quickly, for example, a next-day interview or immediate start.
- The usual requirements of the job (years of experience, qualifications, etc.) don’t match up with what the company is asking for.
- It just seems too good to be true — for example, a fun, in-demand job with good pay that is willing to hire any candidate.
A step by step guide to avoiding job scams
If you suspect that you may be looking at a fake job, here‘s what to do:
- Perform an online search. If you’ve never heard of a company or a recruiter, a quick LinkedIn or Google search should reveal their background.
- Go directly to the company website. If you spot an ad on a third party website, take a look at the company’s website or LinkedIn to make sure it’s the real deal.
- Check the URL. If a website address doesn’t seem right, type it into your browser directly instead of following a link. Most secure websites start with “https://” but this isn’t always a guarantee — a lot of job scams use realistic-looking addresses. If you’re still unsure, look it up on WHOIS.
- Never hand over your money. Legitimate companies will never, ever ask you to pay them money for a job. Even jobs that require you to purchase your own equipment will withhold that money from your paycheck, not ask for it upfront.
- Avoid wire transfers and checks. Direct deposit is the safest way to get paid. If you do get paid by check, never transfer any money out of your account until it clears.
- Don’t hand over personal information before you start. You should be providing details like your bank account information during onboarding, not before you’ve even started the job.
- Take your time. If a recruiter is pushing you to act fast, resist the pressure. Normal hiring processes can take weeks or even months, so don’t let yourself be rushed into making bad decisions.
- Reject suspicious offers. Landing a high level job with zero experience or getting an offer before you’ve even applied seems unlikely for a reason. Stay away from anything that just doesn’t feel right.
- Get a second opinion. Still feel weird about it? Ask someone you trust for a quick gut check. If they’re not sure, either, your instincts may be telling you something.
Where to find real jobs
Sick of wading through the minefield of fake job postings and potential scams? Here's how to find legitimate jobs, every time.
- Apply directly. The best way to avoid a scam is to apply directly through the company website — this also ensures that your resume goes straight to the hiring manager and is less likely to get lost in third-party red tape.
- Use reputable job boards. Bigger job sites, like Indeed, aren't totally immune to scams, but they're more likely to be flagged and removed than on "anything goes" websites like Craigslist or non-job focused social media websites. Smaller, industry-specific job boards are also fairly reliable.
- Rely on your network. Asking someone you know or connecting with recruiters directly on LinkedIn is the best way to find out if something's legit.
What to do if you spot a scam
Think you may have found a job scam — or even fallen for one? Your best course of action is to contact the FTC by calling 1-877-382-4357 or filing an online complaint.