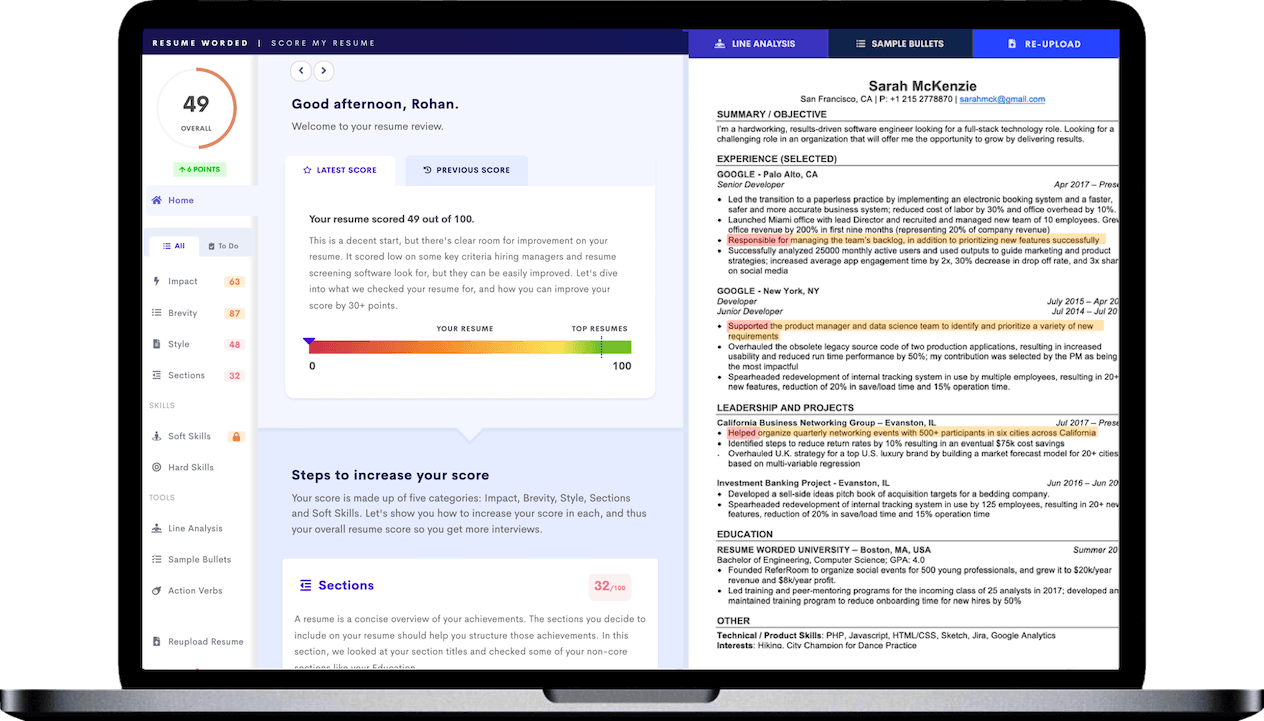
The skills section is a small part of your resume — but that doesn’t mean you should ignore it. While a typical skills list will only be a short section toward the bottom of the page, it’s also one that hiring managers use to quickly see whether you’re a good fit for the job you’re applying for.
But how can you include all your most important skills without letting your Skills section become overcrowded? By using skill categories! Keep reading as we discuss the best way to group skills together, essential tips to keep in mind, and examples of specific-yet-versatile skill categories you can use on your own resume.
Understanding skill categories: What they are and why they're essential
Skill categories are related skills that you can group together on your resume under a single subheading. Generally, you should stick to 2-3 different categories. The skill categories themselves should be:
- relevant to the job you’re applying for, and
- accurately describe the skills you possess
For example, if you were applying for a technical role, instead of listing 10-15 individual hard skills, you might opt to separate your skills into categories like ‘Programming Languages’ and ‘Database Management.’
How to group skills together
Wondering about the best way to group skills together on your resume? You can try:
Grouping skills by job-specific demands
If you’re applying for a job that requires a broad skill set, you can help your resume feel more coherent by separating different skills into different subheadings. For example, if you’re applying for a position as a Project Manager in a technical field, you might want separate skill categories for programming and project management skills.
Example:
- Project Management: Jira, Confluence, Agile, Kanban
- Programming: SQL, MATLAB, Java, Python
Grouping complementary skills
If your skills are more interrelated, you may prefer to group skills into slightly broader categories. This is a good way to group different but related skills like design, modeling, and programming and allows you to elaborate on your skills in more detail.
Example:
- Visual Design: Figma, Sketch, Photoshop
- 3D Modeling and 2D Drafting: Rhino, VRay, AutoCAD
Grouping skills by functional domain
If you’re in a highly specialized field, it may feel more difficult to separate your skills into categories. In this case, you may want to group your skills based on function rather than area. This allows you to provide a comprehensive list of skills that’s still easy for recruiters to skim.
Example:
- Analytics: SQL, R, Python, Predictive Modeling, A/B testing, Java, C++, C#
- Product: Jira, JavaScript, HTML, CSS
Choosing all-purpose skill categories
If you’re not certain what skill categories are best suited to your field — or if you’re just starting out in your career and still narrowing down your options — you might want to go with skill categories that can be easily adapted to different roles and industries.
Example:
- Technical Skills: Microsoft Access, QuickBooks, Blackboard Software, Data Entry Software, Adobe Acrobat Pro
- Languages: English (Native), German (Fluent), French (Conversational)
Why you should categorize skills on your resume
What are the benefits of grouping skills on your resume? Skill categories allow for:
- Improved readability. Separating your skills into smaller categories with subheadings makes them easier to skim and reduces the likelihood that a hiring manager will miss something essential.
- Coherent narrative. Listing everything under a single heading can sometimes look a bit like a jumbled mess, especially if you have a broad skill set. Using skill categories gives your skills list a clear direction.
- Tailoring. Skill categories allow you to easily tailor your resume to different roles or industries and ensure that your skills align with the job description. For example, your resume for a marketing position might group skills into ‘Digital Marketing,’ ‘Content Creation,’ and ‘Analytics,’ while your resume for a customer service role might list nearly the same skills but in categories like ‘Customer Relationship Management (CRM),’ ‘Data Analytics,’ and ‘Communication and Collaboration Tools.’
- Highlighting key skills. The categories you choose can sometimes be as important as the skills themselves. If you’re applying for a job where software development and data analysis are listed as must-have skills, using these as subheadings emphasizes that your skills are a good fit for the role.
- ATS optimization. Applicant Tracking Systems (ATS) work by scanning your resume for keywords, and skill categories allow you to include these in a natural way. For example, if you’re applying for a Software Engineer position, explicitly listing skill categories like ‘Programming Languages,’ ‘Software Development,’ and ‘Algorithm Design’ increase your chances of scoring a high match with the ATS algorithm.
- Impactful presentation. The content of your resume is what matters most, but having a clean, well-designed layout helps more than you might think.
Tips for selecting relevant skill categories
If you’re not sure how to go about categorizing skills on your resume, here are some options you should keep in mind.
Take skills directly from the job description
Any time you’re having trouble deciding how to organize your skills, the best place to start is with the job description. Look for what types of skills the ad emphasizes — for example, if customer service is a major aspect of the position, consider a skill category that relates to customer relationship management.
Incorporate specific keywords
For an even more targeted approach, try to use keywords from the job description verbatim in your resume. For example, if the job ad contains multiple references to ‘data analysis’ and ‘project management,’ consider using those as your subheadings.
You can also utilize the keywords tool below to generate a list of job-relevant hard skills for the position you're applying for.
Adjust your skill categories to different roles
Applying for jobs across multiple roles or industries doesn’t mean you need to change up your resume every time. Skill categories are a quick but highly visible way to tailor your resume — for example, swapping out ‘Social Media Strategy,’ ‘SEO,’ and ‘Content Marketing’ in a digital marketing resume for ‘Project Management’ and ‘Data Visualization’ in one focused on a more managerial role.
Examples of skill categories for different jobs
Looking to dive right in? Here are some suggested skill categories you can add to your resume.
Graphic design
- Visual Design: Adobe Photoshop, Adobe Illustrator, Sketch, Figma, CorelDRAW
- Illustration: Adobe Illustrator, Affinity Designer, Procreate, Clip Studio
- Motion Graphics: Adobe After Effects, Cinema 4D, Blender, Maya
Software development
- Web Development: HTML5, CSS3, JavaScript, React.js, Angular
- Backend Development: Python, Node.js, Java
- Mobile App Development: Swift, Kotlin, React Native
Data analysis
- Data Analysis Tools: Python, SQL, Tableau, Power BI
- Statistical Analysis: Regression Analysis, Hypothesis Testing, ANOVA, Time Series Analysis
- Data Visualization: Tableau, ggplot2, Matplotlib, D3.js, Plotly
Marketing
- Digital Marketing: SEO Optimization, Google Analytics, Facebook Ads, LinkedIn Ads
- Email Marketing: MailChimp
- Marketing Automation: HubSpot, Marketo, ActiveCampaign
Finance
- Technical Skills: Accounting, Forecasting, Budgeting, Auditing, Invoicing
- Industry Knowledge: Projection Modeling, Market Analysis, Risk Identification and Analysis
- Tools and Software: SAP Products, Microsoft Power BI, Hyperion, Tableau, Essbase
Engineering
- Structural Engineering: AutoCAD, SAP2000, ETABS, Revit Structure
- Geotechnical Engineering: PLAXIS, GeoStudio, LPILE
- Project Management: Microsoft Project, Primavera P6, Procore